Objective
Internet Protocol Security (IPSec) provides secure tunnels between two peers, such as two routers. Packets that are considered sensitive and should be sent through these secure tunnels, as well as the parameters that should be used to protect these sensitive packets should be defined by specifying the characteristics of these tunnels. Then, when the IPsec peer sees such a sensitive packet, it sets up the appropriate secure tunnel and sends the packet through this tunnel to the remote peer.
Cisco ASA5500 – L2TP over IPSEC VPN https://www.petenetlive.com/KB/Article/0000571. I was experimenting with L2TP/IPsec connections between a Windows 10 PC and a Mikrotik router on the other day. Analyzing the debug level log of the Mikrotik I figured out that Windows 10 (version 1511) is offering the following authentication and encryption settings during the key exchange (in this priority order): SHA1 + AES-CBC-256 + ECP384. Yes, all other clients (L2TP/IPSec Cisco client, Windows 7, iOS, Mac OS X, etc.) are able to connect properly. Only Win 10 clients cannot. – Dave Sep 30 '16 at 20:45 When the client attempts to connect what do the asa logs and debug crypto isakmp 100 and debug crypto ipsec 100 show? This is a message to Microsoft from the IT community at large. With the increased difficulty of making the now defunct Cisco IPsec VPN Client work on Windows 10, we would really like to see Microsoft come to the table with a solution for connecting to infrastructures that use Group Authentication. Note: You will be taken back to the IPSec Profiles Table and the newly-created IPSec profile should now appear. (Optional) To save the configuration permanently, go to the Copy/Save Configuration page or click the icon at the upper portion of the page.
When IPsec is implemented in a firewall or a router, it provides strong security that can be applied to all traffic crossing the perimeter. Traffic within a company or workgroup does not incur the overhead of security-related processing.

The objective of this document is to show you how to configure the IPSec Profile on an RV34x Series Router.
Applicable Devices
- RV34x Series
Software Version
- 1.0.1.16
Configure IPSec Profile
Create an IPSec Profile
Step 1. Log in to the web-based utility of the router and choose VPN > IPSec Profiles.
Step 2. The IPsec Profiles Table shows the existing profiles. Click Add to create a new profile.
Step 3. Create a name for the profile in the Profile Name field. The profile name must contain only alphanumeric characters and an underscore (_) for special characters.
Note: In this example, IPSec_VPN is used as the IPSec profile name.
Step 4. Click a radio button to determine the key exchange method the profile will use to authenticate. The options are:
- Auto — Policy parameters are set automatically. This option uses an Internet Key Exchange (IKE) policy for data integrity and encryption key exchanges. If this is chosen, the configuration settings under the Auto Policy Parameters area are enabled. Click here to configure the Auto settings.
- Manual — This option allows you to manually configure the keys for data encryption and integrity for the Virtual Private Network (VPN) tunnel. If this is chosen, the configuration settings under the Manual Policy Parameters area are enabled. Click here to configure the Manual settings.
Note: For this example, Auto was chosen.
Configure the Auto Settings
Step 1. In the Phase 1 Options area, choose the appropriate Diffie-Hellman (DH) group to be used with the key in Phase 1 from the DH Group drop-down list. Diffie-Hellman is a cryptographic key exchange protocol which is used in the connection to exchange pre-shared key sets. The strength of the algorithm is determined by bits. The options are:
- Group2 - 1024 bit — Computes the key slower, but is more secure than Group1.
- Group5 - 1536-bit — Computes the key the slowest, but is the most secure.
Note: In this example, Group2-1024 bit is chosen.
Step 2. From the Encryption drop-down list, choose the appropriate encryption method to encrypt and decrypt Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) and Internet Security Association and Key Management Protocol (ISAKMP). The options are:
- 3DES — Triple Data Encryption Standard.
- AES-128 — Advanced Encryption Standard uses a 128-bit key.
- AES-192 — Advanced Encryption Standard uses a 192-bit key.
- AES-256 — Advanced Encryption Standard uses a 256-bit key.
Note: AES is the standard method of encryption over DES and 3DES for its greater performance and security. Lengthening the AES key will increase security with a drop-in performance. For this example, AES-256 is chosen.
Step 3. From the Authentication drop-down menu, choose an authentication method that will determine how ESP and ISAKMP are authenticated. The options are:
- MD5 — Message Digest Algorithm has a 128-bit hash value.
- SHA-1 — Secure Hash Algorithm has a 160-bit hash value.
- SHA2-256 — Secure Hash Algorithm with a 256-bit hash value.
Note: MD5 and SHA are both cryptographic hash functions. They take a piece of data, compact it, and create a unique hexadecimal output that is typically not reproducible. In this example, SHA2-256 is chosen.
Step 4. In the SA Lifetime field, enter a value ranging between 120 to 86400. This is the length of time the Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Security Association (SA) will remain active in this phase. The default value is 28800.
Note: In this example, 28801 is used.
Step 5. (Optional) Check the Enable Perfect Forward Secrecy check box to generate a new key for IPSec traffic encryption and authentication.
Step 6. From the Protocol Selection drop-down menu in the Phase II Options area, choose a protocol type to apply to the second phase of the negotiation. The options are:
- ESP — If this is chosen, skip to Step 7 to choose an encryption method on how the ESP packets will be encrypted and decrypted. A security protocol which provides data privacy services and optional data authentication, and anti-replay services. ESP encapsulates the data to be protected.
- AH — Authentication Header (AH) is a security protocol which provides data authentication and optional anti-replay services. AH is embedded in the data to be protected (a full IP datagram). Skip to Step 8 if this was chosen.
Step 7. If ESP was chosen in Step 6, choose the appropriate encryption method to encrypt and decrypt ESP and ISAKMP from the Encryption drop-down list. The options are:
- 3DES — Triple Data Encryption Standard.
- AES-128 — Advanced Encryption Standard uses a 128-bit key.
- AES-192 — Advanced Encryption Standard uses a 192-bit key.
- AES-256 — Advanced Encryption Standard uses a 256-bit key.
Note: In this example, AES-256 is chosen.
Step 8. From the Authentication drop-down menu, choose an authentication method that will determine how ESP and ISAKMP are authenticated. The options are:
- MD5 — Message Digest Algorithm has a 128-bit hash value.
- SHA-1 — Secure Hash Algorithm has a 160-bit hash value.
- SHA2-256 — Secure Hash Algorithm with a 256-bit hash value.
Note: In this example, SHA2-256 is used.
Step 9. In the SA Lifetime field, enter a value ranging between 120 to 28800. This is the length of time the IKE SA will remain active in this phase. The default value is 3600.
Note: In this example, 28799 is used.
Step 10. From the DH Group drop-down list, choose the appropriate Diffie-Hellman (DH) group to be used with the key in Phase 2. The options are:
Windows Native VPN Client - Networking
- Group2 – 1024 bit — Computes the key slower, but is more secure than Group1.
- Group5 – 1536 bit — Computes the key the slowest, but is the most secure.
Note: In this example, Group5 – 1536 bit is chosen.
Step 11. Click .
Note: You will be taken back to the IPSec Profiles Table and the newly-created IPSec profile should now appear.
Step 12. (Optional) To save the configuration permanently, go to the Copy/Save Configuration page or click the icon at the upper portion of the page.
You should now have successfully configured an Auto IPSec Profile on an RV34x Series Router.
Configure the Manual Settings
Step 1. In the SPI-Incoming field, enter a hexadecimal number ranging from 100 to FFFFFFF for the Security Parameter Index (SPI) tag for incoming traffic on the VPN connection. The SPI tag is used to distinguish the traffic of one session from the traffic of other sessions.
Note: For this example, 0xABCD is used.
Ipsec On Windows 10
Step 2. In the SPI-Outgoing field, enter a hexadecimal number ranging from 100 to FFFFFFF for the SPI tag for outgoing traffic on the VPN connection.
Note: For this example, 0x1234 is used.
Step 3. Choose an option from the Encryption drop-down list. The options are 3DES, AES-128, AES-192, and AES-256.
Note: In this example, AES-256 is chosen.
Step 4. In the Key-In field, enter a key for the inbound policy. The key length depends on the algorithm chosen in Step 3.
- 3DES uses a 48-character key.
- AES-128 uses a 32-character key.
- AES-192 uses a 48-character key.
- AES-256 uses a 64-character key.
Note: In this example, 123456789123456789123… is used.
Step 5. In the Key-Out field, enter a key for the outgoing policy. The key length depends on the algorithm chosen in Step 3.
Note: In this example, 1a1a1a1a1a1a1a121212… is used.
Step 6. Choose an option from the Manual Integrity Algorithm drop-down list.
- MD5 — Uses a 128-bit hash value for data integrity. MD5 is less secure but faster than SHA-1 and SHA2-256.
- SHA-1 — Uses a 160-bit hash value for data integrity. SHA-1 is slower but more secure than MD5, and SHA-1 is faster but less secure than SHA2-256.
- SHA2-256 — Uses a 256-bit hash value for data integrity. SHA2-256 is slower but secure than MD5 and SHA-1.
Note: In this example, MD5 is chosen.
Step 7. In the Key-In field, enter a key for the inbound policy. The key length depends on the algorithm chosen in Step 6.
- MD5 uses a 32-character key.
- SHA-1 uses a 40-character key.
- SHA2-256 uses a 64-character key.
Note: In this example, 123456789123456789123… is used.
Step 8. In the Key-Out field, enter a key for the outgoing policy. The key length depends on the algorithm chosen in Step 6.
Note: In this example, 1a1a1a1a1a1a1a121212… is used.
Step 9. Click .
Note: You will be taken back to the IPSec Profiles Table and the newly-created IPSec profile should now appear.
Step 10. (Optional) To save the configuration permanently, go to the Copy/Save Configuration page or click the icon at the upper portion of the page.
You should now have successfully configured a Manual IPSec Profile on an RV34x Series Router.
Windows 8 and newer easily support IKEv2 VPNs, and Windows 7 can as well thoughthe processes are slightly different. The procedure in this section wasperformed on Windows 10, but Windows 8 is nearly identical. The procedure toimport certificates to Windows 7 can be found on the strongSwan Wiki
Import the CA to the Client PC¶
Export the CA Certificate from pfSense® and download or copy it to the clientPC:
Navigate to System > Cert Manager, Certificate Authorities tab onpfSense
Click by the CA to download only the certificate
Locate the downloaded file on the client PC (e.g. VPNCA.crt) as seen in FigureDownloaded CA Certificate
Double click the CA file
Click Install Certificate… as shown inCertificate Properties
Certificate Properties¶
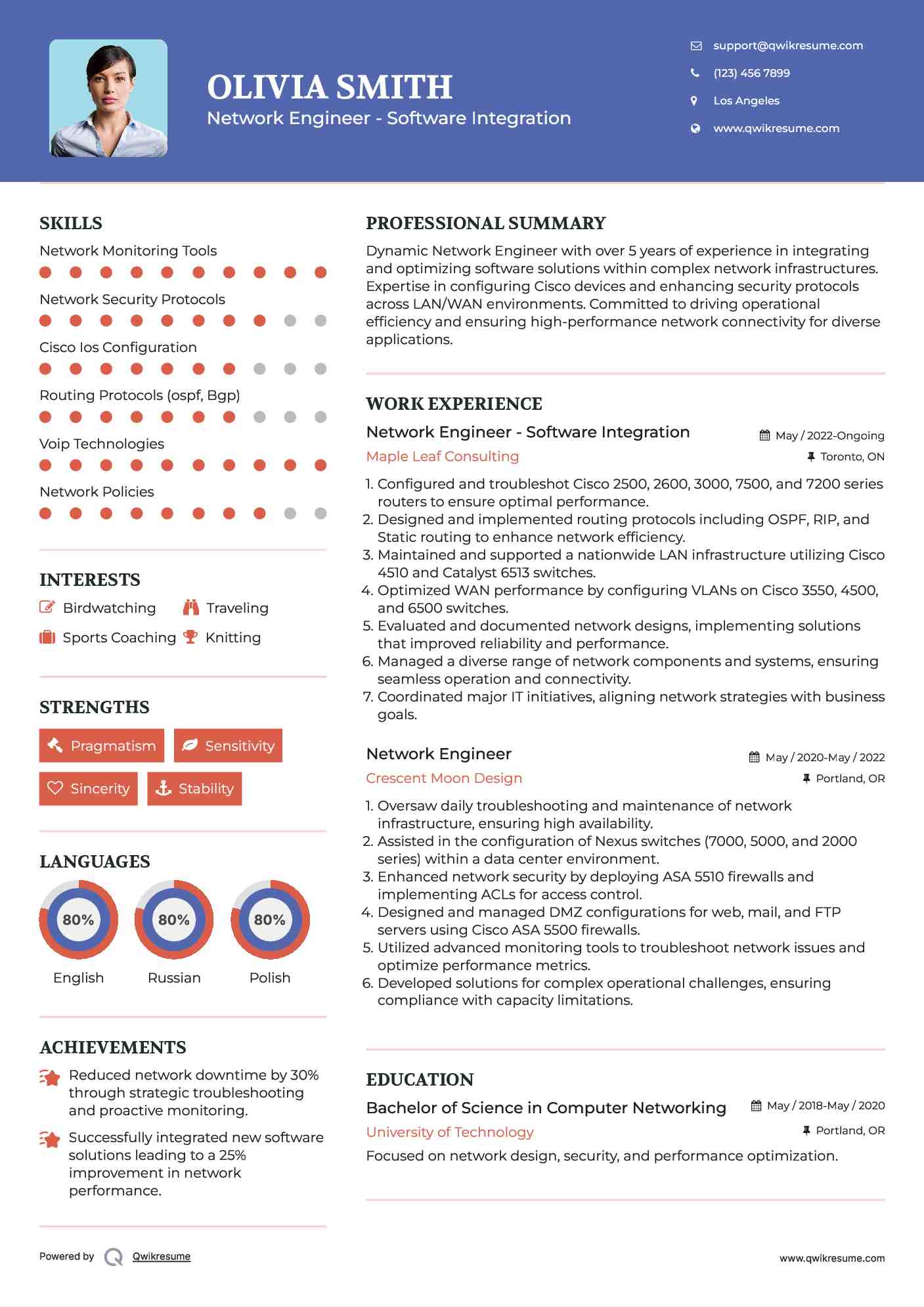
Select Local Machine as shown inCertificate Import Wizard - Store Location
Click Next
Click Yes at the UAC prompt if it appears
Select Place all Certificates in the following store as shown in FigureCertificate Import Wizard - Browse for the Store
Certificate Import Wizard - Browse for the Store¶
Click Browse
Click Trusted Root Certification Authorities as shown in FigureSelect Certificate Store
Click Next
Review the details, they should match those in FigureCompleting the Certificate Import Wizard
Completing the Certificate Import Wizard¶
Click Finish
Click OK
Click OK
Setup the VPN Connection¶
Once the certificate has been properly imported it is time to create the clientVPN connection. The exact steps will vary depending on the version of Windowsbeing used by the client, but will be close to the following procedure.
Open Network and Sharing Center on the client PC
Click Set up a new connection or network
Select Connect to a workplace
Click Next
Select No, create a new connection
Click Next
Click Use my Internet Connection (VPN)
Enter the IP address or hostname of the server into the Internet addressfield as shown in FigureWindows IKEv2 VPN Connection Setup Screen
Note
This must match what is in the server certificate Common Name or a configured Subject Alternative Name!
Enter a Destination Name to identify the connection
Click Create
The connection has been added but with several undesirable defaults. For examplethe type defaults to automatic. A few settings need to be set by hand firstto ensure a proper connection is made. Refer to FigureWindows IKEv2 VPN Connection Properties
In Network Connections / Adapter Settings in Windows, find theconnection created above
Right click the connection
Click Properties
Click the Security tab
Set Type of VPN to IKEv2
Set Data Encryption to Require Encryption (disconnect if serverdeclines)
Set Authentication / Use Extensible Authentication Protocol to Microsoft:Secured password (EAP-MSCHAP v2) (encryption enabled)
Compare the values on the screen to those in FigureWindows IKEv2 VPN Connection Properties
Click OK
Windows IKEv2 VPN Connection Properties¶
The connection is now ready to use.
Disable EKU Check¶
When the CA and server certificates are made properly on pfSense 2.2.4 andlater, this is not necessary. If an improperly generated server certificate mustbe used for some reason, then the Extended Key Usage check may need to bedisabled on Windows. Disabling this check also disables validation of thecertificate’s common name and SAN fields, so it is potentially dangerous. Anycertificate from the same CA could be used for the server when this is disabled,so proceed with caution.

To disable the extended key usage checks, open up Registry Editor on the Windowsclient and navigate to the following location in the client registry:
In there, add a new DWORD entry named DisableIKENameEkuCheck and set itto 1.
A reboot may be required to activate the setting.
Advanced Windows IPsec settings¶
Cisco Ipsec Vpn Client Windows 10
With Windows 10 PowerShell cmdlet Set-NetIPsecMainModeCryptoSet it is possible tochange various advanced settings, like IPsec lifetime:
This example modifies the maximum IPsec SA lifetime for the “pfSense IPsec” connection.The default Windows IPsec lifetime is 4800 minutes (eight hours).
See also
Use Shrew Soft VPN Client To Connect With IPSec VPN ... - Cisco
For more information, see Windows 10 IPsec PowerShell cmdlets
